Nominal Ledger And Cash Book
Purpose: To configure the settings in order that the Nominal Ledger and Cash Book work in the best way, suitable for your business. The form comprises two pages – General settings and Control Accounts – see the Nominal Ledger Control Accounts article for more information.
General Page
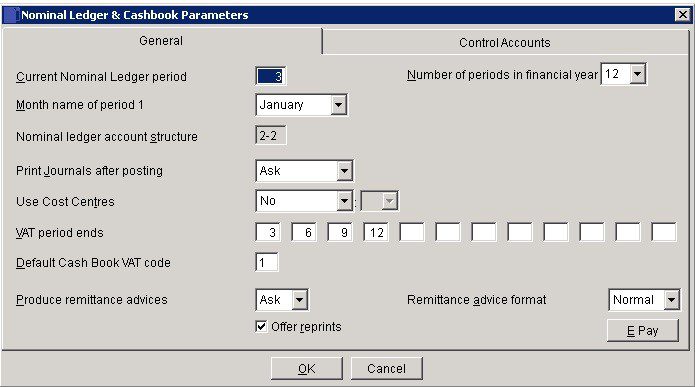
- Period: 1. Enter a number from 1 to 12 corresponding to the current Nominal Ledger period; keeping in mind the Period Rule (see Period End Processing). This should only be changed when there are no transactions in the system, such as when setting up a new company.
- Enter the number of reporting periods within a financial year.
- Select from the drop-down box the month name which corresponds to the first month of your financial year.
- Nominal Structure: As with all records in the system, a Nominal Account requires a unique code – see Tables, Records, Forms and Fields.
- First time users might find it useful to consult your Prelude Desktop distributor for further advice on how to design an Account Code structure appropriate to their business management needs. Nominal Account Codes have a two-level structure, comprising a total of 8 characters in two groups separated by a dash. Each group must contain a minimum of two alphanumeric characters, and can contain up to 6 characters. The group of characters to the left of the dash identifies the top level of the code called the Head or Group Code. The second group of characters identifies the bottom level, called the Tail or Account Code.
- A list of all these codes set up in the system is called the Chart of Accounts.
- As an example: The Group Code ‘CA’ is used for Current Assets on the Balance Sheet. The individual Accounts are sub-grouped by the remaining two characters – CA04 for Current Assets – Bank, CA02 for Current Assets – Debtors Control etc.
The system comes pre-installed with a Chart of Accounts for immediate use.
- Cost Centres: For additional analysis for departments, divisions or even individuals – set default – usually 00.
- Cash Book VAT Code: Default VAT code from VAT Codes list to be used when analysing Nominal Receipts and Payments.
- Remittances: Select Yes if you always want print a remittance advice during Cash Book Purchase Ledger payment entry, No if you never want to print or Ask if you want to be asked after each payment has been entered. Select which document format to use for the advices: the normal format or the cheque format.
- E-Pay: – see below.
- Click ‘OK’ to save or ‘Cancel‘ to clear and close without saving.
E-Pay Button Page
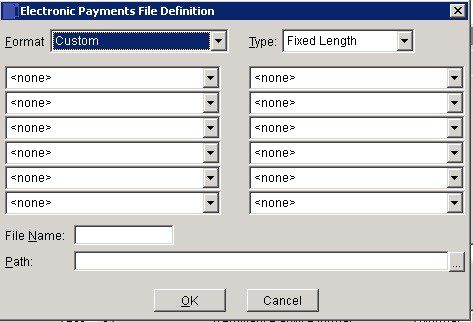
Use this to allow payments to be made directly to Suppliers’ Bank Accounts – use this instead of cheque payments to save both time and money. Contact your bank for details of the data required by them in order to transact payments electronically. Once the bank have responded, we recommend that you ensure relevant supplier standing data is fully up to date – one way to do this is to canvass suppliers to confirm their details.
- Click the drop down boxes to select one each of up to 12 data fields.
- Click the Type drop down and select the required file format from one of either Fixed, Fixed Length or Comma Separated Values (CSV). Contact your bank if you are unsure as to which format to use.
- Enter a file name using up to 8 alphanumeric characters
- Click OK to close form and save your selection.
- Before using this to pay a supplier ensure the payment method is ‘E’ – see Supplier Account – Miscellaneous Page for details.
- Click ‘OK’ to save or ‘Cancel’ to clear and close without saving.
Control Accounts Page
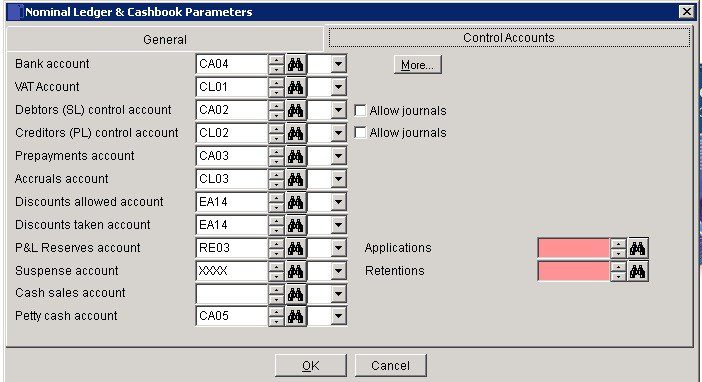
The Nominal Ledger control accounts must be correctly configured before using your software product as the system posts data automatically to these accounts. For example when posting an invoice, all VAT is posted to the VAT Account and the total invoice value is posted to the Sales Ledger control account – You only have to choose where to post the net amount for analysis and management information.. Ensure that all appropriate codes have been created in the nominal ledger before entering nominal codes in the fields – see Add & Edit Nominal Accounts
- Bank Account – This is the main bank account as defined in Company Details. Other bank accounts can be added by clicking on More. CCY displays the home currency if currency module is activated. See Create Multiple Bank Accounts
- The VAT account controls your VAT Liability.
- The SL & PL Control Accounts reflect a summary of all the individual customer and supplier. The Aged Debtor and Aged Creditor reports totals should agree to these accounts balances.
- Allow journals – allows journals to be made to the Control Accounts – should only be used by a competent bookkeeper with good reason.
- Accruals and Prepayments accounts are used to adjust transactions that cover more than one period are adjusted to reflect the cost for that period.
- Discounts are taken from the cash book to adjust for differences between the value of invoices being paid and the bank amount.
- The Reserves account is used to transfer profits and losses at year end so that the Profit and loss is cleared for the following year.
- The Suspense account is used by the system if imbalances occur so that they can be corrected and is available to the user to store items where more information is needed before being able to code to the right account.
- Cash Sales and Petty Cash accounts – similar to bank accounts but with care needed when posting transactions between these accounts and bank accounts to avoid duplication.
- Exchange Rate Differences – Shows only when the currency option is activated – see Use the Currency Module.
- Additional Control accounts may be added from other Business Processing modules such as Applications and Retentions from the costing module.
- Click ‘OK’ to save or ‘Cancel’ to clear and close without saving.

0 Comments